Cryptocurrencies vs. Traditional Currencies: Key Differences
Cryptocurrency, also known as virtual currency, is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptographic technology to ensure transaction security.
Unlike traditional currencies like the U.S. dollar, cryptocurrencies are typically not issued by any central authority, and their core characteristics include decentralization, transparency, and data immutability.

Origins of Cryptocurrency
The concept of cryptocurrency can be traced back to the concept of “electronic cash” proposed by American cryptographer, David Chaum, in 1983.
However, not until the release of the Bitcoin whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” in 2009, by a mysterious individual (or group) known as Satoshi Nakamoto did the cryptocurrency truly come into existence.
The emergence of Bitcoin marked the creation of the first decentralized cryptocurrency, designed to establish a payment system independent of central authorities.
Core Technology of Cryptocurrency: Blockchain
The core technology behind cryptocurrencies is blockchain, a decentralized database that records all transactions maintained through a network of distributed nodes.
Once a transaction is confirmed, it is permanently recorded in a “block” on a digital ledger. Each new block is linked to the previous one, forming a chain known as a “blockchain.”
Characteristics of Cryptocurrency
The characteristics (advantages) of cryptocurrencies are mainly shown in their unique technical architecture and operational methods, which make them distinct from traditional monetary systems. Some of the key characteristics of cryptocurrencies are as follows.
1. Decentralization
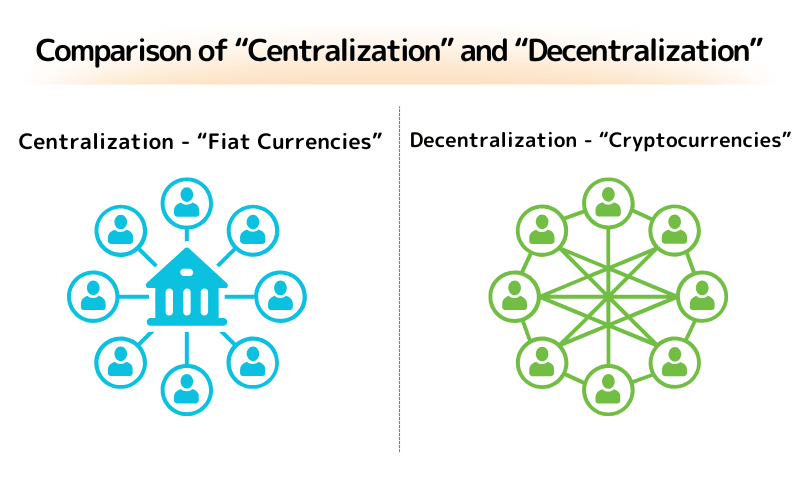
One of the major characteristics of cryptocurrencies is their decentralized nature, meaning they do not rely on any central authority (such as a central bank or government) for issuance or management.
Instead, cryptocurrencies are operated through a decentralized network of nodes, each holding a complete transaction record, which enhances system transparency and resistance to censorship.
2. Cryptographic Security
Cryptographic technology is also the core of cryptocurrencies, ensuring transaction security, and preventing fraud and double spending.
These technologies include the system of public keys and private keys. The public key is used to receive funds, while the private key is used to sign transactions, ensuring both transaction security and user confidentiality.
3. Transparency
All cryptocurrency transactions are recorded on public blockchains, which anyone can access without permission.
This transparency ensures the traceability and verifiability of transactions, thereby enhancing trust in the network.
4. Immutability
Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it is almost impossible to alter or delete it.
Each new block builds upon the previous one, creating a continuous chain, making it extremely difficult to retrospectively change the records in the past.
5. Limited Supply
Many cryptocurrencies (most notably Bitcoin) have a fixed supply limit, meaning only a set amount of currency can be created.
This scarcity emulates precious metals like gold and is regarded as a hedge against inflation.
6. Global Accessibility
Cryptocurrencies are operated on the internet that is free of geographical restrictions, allowing anyone with network access to participate.
This provides financial services to those who may not have effective access to traditional banking systems.
There are various benefits and also various risks using cryptocurrencies, some of the aspects will be discussed as follows.
Risks of Cryptocurrencies
While cryptocurrencies bring new financial instruments and investment opportunities, it also carries risks that cannot be ignored. The main risks are as follows.
1. Price Volatility
Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile, investors may be faced with high risks and high rewards.
Rapid price fluctuations can lead to substantial losses for investors.
2. Regulatory Uncertainty
Many countries are still developing laws and regulations regarding cryptocurrencies, which creates uncertainty.
Policy changes can significantly impact the cryptocurrency market, affecting its price and availability.
3. Technical Risks and Security Issues
Although cryptocurrency itself is highly secure, users must handle keys and funds carefully.
Data breaches, phishing attacks, or other forms of cybercrime could result in asset loss.
Items of Cryptocurrencies
Some major international cryptocurrencies (virtual currencies) along with their uses and characteristics are as follows.
1. Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin, created by the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009, was the first and most well-known cryptocurrency.
It aims to provide an electronic payment system independent of any central bank or single administrator.
With a fixed supply limit of 21 million coins, Bitcoin is often regarded as digital gold, valued for its scarcity and use as a hedge against inflation for value storage.
2. Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum is a cryptocurrency platform focused on the support for smart contracts, self-executing contracts with terms embedded in their codes.
This feature of ETH has created wide possibilities for decentralized applications (DApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi), making ETH the best platform of choice for developers creating blockchain-based applications.
3. Ripple (XRP)
Ripple is a digital currency created by Ripple Labs, mainly designed for cross-border payments and interbank transactions.
Unlike the fully decentralized Bitcoin and Ethereum, Ripple is more centralized, with Ripple Labs controlling the majority of nodes.
Fast transaction speed and low fees make Ripple an ideal choice for banks and financial institutions.
4. Litecoin (LTC)
Litecoin, created in 2011 by former Google engineer Charlie Lee, is often referred to as the “silver” to Bitcoin’s “gold.”
It is technically similar to Bitcoin but offers faster transaction confirmation times and a higher supply cap (84 million coins).
Litecoin is designed to be a digital currency that is more suitable for everyday transactions.
5. Cardano (ADA)
Cardano (ADA) is a relatively new cryptocurrency developed with a method driven by the philosophy of science and research.
The development of ADA is led by Charles Hoskinson, one of the co-founders of Ethereum.
The characteristic of ADA is its layered architecture which allows for rapid processing of the transaction, and also supports smart contracts and various decentralized applications.
6. Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
Bitcoin Cash is created through a hard fork of Bitcoin in 2017, aiming for the increase of block size to allow for more transactions per block, addressing issues of transaction speed and transaction fees for Bitcoin.
Bitcoin Cash provides faster transaction confirmation time, making it a better choice for everyday transactions.
7. Dogecoin (DOGE)
Dogecoin was created in 2013 by Billy Markus and Jackson Palmer, with the Shiba Inu dog meme, “Doge”, as its mascot.
Dogecoin was designed as a more approachable Bitcoin alternative, aiming for the establishment of a friendly community.
Dogecoin is particularly suitable for small payments and tips, given its low transaction fees and quick confirmation time.
Unlike Bitcoin, Dogecoin has no maximum supply cap, making it an inflationary cryptocurrency.
8. Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot is the native currency of the Polkadot network. It was launched in 2020 and was developed under the leadership of Gavin Wood, the co-founder of Ethereum. Polkadot aims to support multi-chain interoperability, allowing seamless data and asset transfers between different blockchains.
The “blockchain of blockchains” structure makes it an ideal platform for cross-chain applications and services.
Polkadot is used for managing/handling inter-chain transaction fees and “parallel chain” operations that connect Polkadot to other blockchains.
9. Chainlink (LINK)
Chainlink is the native currency of the Chainlink network, a decentralized Oracle network designed to connect blockchain technology with real-world data.
Chainlink allows smart contracts to securely access external data sources, events, and payment measures, and this is critical for sectors like financial services, insurance, and supply chain management to realize complex smart contracts. Chainlink is used to pay for various service fees and support the operation of these key functions.
10. Stellar (XLM)
Stellar is the native cryptocurrency of the Stellar network, founded in 2014 by Jed McCaleb, the co-founder of Ripple and Joyce Kim.
Stellar aims to promote the interconnection of global financial systems, it is particularly focused on rapid and low-cost cross-border transactions and micropayments.
With its unique consensus protocol, Stellar not only improved transaction speed, but also effectively reduced cost for transactions, making it particularly attractive to financial services in developing countries.
Stellar is used in the network to pay transaction fees and serves as a bridge for conversion between various currencies, supporting the decentralized financial ecosystem of Stellar network.
Besides the currencies mentioned above, there are still other currencies like TRON (TRX), Zcash and EOS, etc.
Comparison of Cryptocurrencies and Traditional Currencies
The table below highlights the major differences between cryptocurrencies and traditional fiat currencies (e.g., USD, EUR).
| Item | Cryptocurrencies | Traditional Currencies |
|---|---|---|
| Issuing agency | Decentralized, typically controlled by algorithms and network consensus mechanisms. | Centralized, issued by governments and central banks |
| Physical Form | Digital only | In both physical (cash, coins) and digital forms |
| Transaction Speed | Varies from seconds to minutes based on blockchain technology | Digital transfers may take minutes to days; cash transactions is immediate |
| Transaction Fees | It depends, can be very low but may significantly increase during network congestion. | Generally set by banks or financial institutions, there is a fixed range for it. |
| Security | Relies on cryptographic technology, theoretically highly secure | Relies on laws, physical, and digital security measures |
| Transparency | Public transaction records that cannot be altered | Transaction records kept private by banks |
| Accessibility | Available to anyone with internet access | Requires a bank account or similar financial services |
| Value Stability | Highly volatile, pricing by demand-supply of the market | Relatively stable, controlled by policies and economic conditions |
CFD (Contract for Difference) Trading of Cryptocurrencies
At Titan FX, investors can engage in cryptocurrency CFD trading, including major digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin, with a leverage of up to 100x for long or short positions.
Titan FX also provides competitive spreads, low trading costs, and a variety of analytical tools.
Learn more about cryptocurrency trading with Titan FX.Summary and Outlook
Since Bitcoin’s debut in 2009, cryptocurrencies have evolved from an experimental digital asset into a global financial phenomenon.
Thousands of cryptocurrencies are now circulating in the market, widely adopted by individuals, businesses, and even governments all over the world.
With continuous technological advancements, cryptocurrency has the potential to bring a further revolution to the financial industry, particularly with the potential for aspects of increasing financial inclusion, expediting funds transfer, and promoting financial innovation.
As cryptocurrencies gradually integrate into the broader financial system, educating and informing the public will be crucial to support healthy market development. In the future, it is estimated that cryptocurrency and its fundamental technique, blockchain, will lead the development of smart contracts, decentralized finance (DeFi), and more decentralized applications (DApps).
However, as this type of asset gradually becomes the choice of mainstream investment option, its long-term impact on economic stability, privacy protection, and regulatory formulation still requires further observation and research.
Under this background, the CFD trading of cryptocurrencies provided by Titan FX allows investors to trade dynamic digital assets including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin, with leverage of up to 100 times.
This not only provides traders with a flexible way to enter the cryptocurrency market, but also emphasizes the importance of risk management.
Investors and market participants need to fully understand the potential and risks of these financial instruments in order to make informed decisions.
As cryptocurrencies are gradually integrated into a broader financial system, the universalization of education and information for the public will be crucial to support healthy market development.